
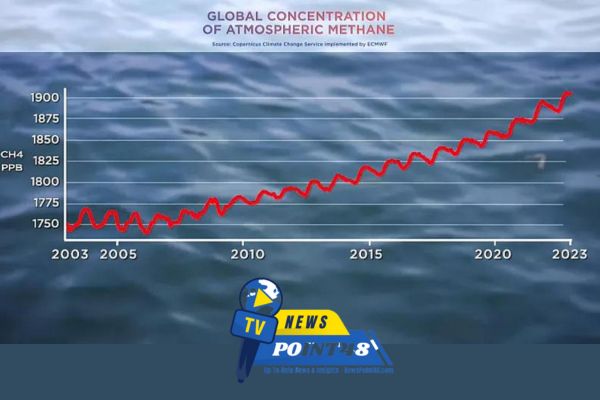
It’s plain simple that in most situations where climate change is the Chronos, then methane emissions are expected to go up to even new highs. This similarity is worrying because methane is much more effective than carbon dioxide in that respect. The latest data suggests that as a consequence of these increases, methane emissions are at their highest point in history, creating a dilemma in the proposed climate change solutions. Here’s a look at where these emissions are coming from and what it means for the global situation.
Methane and Global warming.
Methane (CH₄) is one of the most potent greenhouse gases in the world though it is found in smaller amounts compared to carbon dioxide, in about 100 years CH₄ will outperform CO2 by over 25 times in terms of heat retention. Methane is mostly administered from anthropogenic sources as opposed to natural ones like wetlands. A major source of methane lies in three sectors: agriculture (livestock and rice cultivation), oil and gas industry, waste disposal and treatment.
The reason behind the high levels of Methane.
New research tells us something that we have only suspected for a long time, and that is that it appears that because of a variety of reasons, Edmonton as an example has emitted more than five times than it had over the recent past.
Agricultural Activities: Among the agricultural activities livestock farming or more specifically cattle keeping is a large methane emitter due to cattle enteric fermentation and methane from rice paddies too.
Methane Emission and Its Sources: Fossil energy resources such as oil, gas, and coal are obtained, processed, and distributed which involves a high level of emission of methane. Such emissions are particularly attributable to the leakage of gas from wells and pipelines.
Waste Management: Similarly, landfills or waste disposal sites and facilities that treat wastewater also produce methane because the solid organic materials in these places undergo anaerobic decomposition.
People and businesses have been very aware of these emissions but their efforts to contain these emissions have not lowered the emissions very much, simply because most countries do not have the necessary rules or the required technology within the country which is required to collect and reduce the emissions of Methane.
The Threat to Global Climate Goals

Buffering against temperature increases, diary of comments on in situ monitoring. The increase of these gases into the atmosphere, however, poses a dangerous threat to this goal which the COP21 Paris Agreement seeks to achieve. Pressure when methane stays in a space and cannot escape propagates global warming at a particular gas which is more quickly than when only carbon dioxide content is added.
Dairy farming and constraints on greenhouse gas emissions methane. If we do, steady greenhouse gas emissions will overheat the world, and paradigm temperatures the semi-arid regions cannot withstand will be reached much earlier than usually z offered in logic, which means worse and worse weather conditions, increased waters that are better than ocean-level and destruction of native living things ideas.
Mitigation Strategies: What Can Be Done?
The second in the list represents the need to consider sources of methane emissions from all processes that state. Bringing down the levels of methane emissions, therefore, requires understanding that it is a complex issue that involves different approaches to GHG emissions signs and indicators.
Agricultural Development: Changes in the formulation of animal feeds, alteration of livestock waste management and switching of certain rice growing methods will help in decreasing emissions to the agriculture sector.
Eliminating Fossil Fuel Leaks: It is possible to achieve substantial reductions in methane emissions within the fossil fuel sector by introducing more advanced standards, improving business infrastructure, and using more efficient leak detection and repair technology.
Improving Waste Management: In this way, methane that would have been released as waste, can be captured and used as an energy source through the use of biogas technology.
The Impact of Policy and Global Engagement
At the internal and external polity levels, policy measures are necessary to reduce the emissions of methane gas. The Global Methane Pledge was established in COP26 to achieve a 30 % reduction in global methane emissions within the year 2030 in comparison to the year 2020. For achievement of this goal, there will be a need to lay out coordinated interventions, and strong policy platforms as well as allocate resources for all activities geared towards comprehension of methane reduction technologies.
Those countries must also improve their monitoring and reporting of emissions to make certain that there are no excuses for the lack of transparency on the emission effort, including technology transfer and sharing collective knowledge, which will be very important in realizing these ambitious targets.
A Call to Action However, Due to the Circumstances WE Have No Choice But to Urge Immediate Action Methane emissions have reached unprecedented levels, so more drastic actions are demanded to save our climate. These challenges though they are great, can however be solved if all the parties, governments, industries, and societies unite together. Cutting back on methane emissions is one of the simplest and fastest methods for taking control of global warming and keeping climate objectives achievable.
